Knowledge base
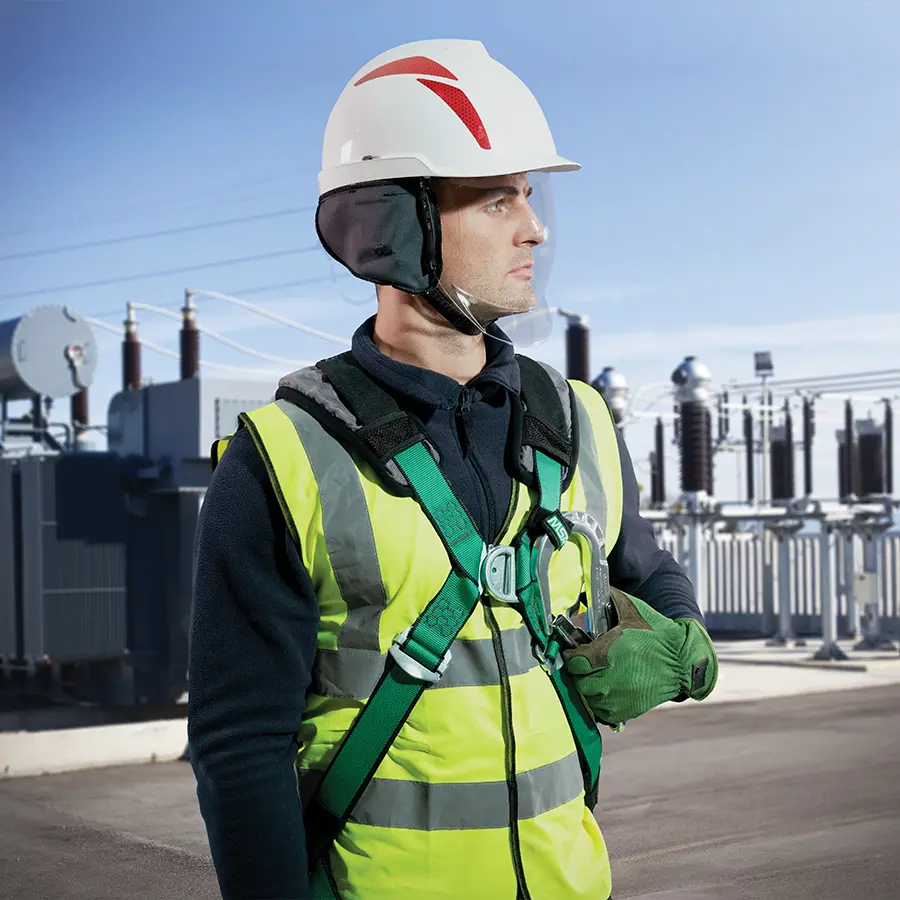
Protected working with high voltage
Dangers of high voltage
Working with high voltage involves several dangerous risks, which can cause serious injury and sometimes even death. The two risks we will focus on in this article are:
- Electrocution: high voltage can cause electric shock, which varies in severity depending on the amperage and duration of exposure. Even small amounts of current can be life-threatening.
- Arc Flashover: arc flashovers (also known as “arc flashes”) involve extreme temperatures, bright flashes of light, flying (molten) shrapnel, pressure waves with loud bangs and toxic copper fumes. This can lead to serious risks to workers, including internal and external burns, blindness, hearing damage and copper poisoning from inhaled gases.
Important standards around high voltage
The above hazards show that the entire body is at risk of injury from electrocution or an arc. Protective clothing, head protection and arm and hand protection is therefore essential. These types of PPE come with some important standards that must be met.
Clothing: IEC 61482-2

This is an international standard specifically aimed at protecting workers from the thermal hazards of an electric arc in case of exposure. Within this standard, clothing can be tested in 2 ways, namely:
- IEC 61482-1 via the ‘open arc’ test: in this test, test material is struck by an 8kA arc from a distance of 30 cm. The resulting ATPV value (Arc Thermal Performance Value) indicates the amount of energy (cal / cm²) to which the material or garment can be exposed and still provide 50% protection against second-degree burns. The higher this value, the better the protection.
- EN 61482-2 via the “box test”: in this method, an arc is generated from one direction (the box) for a short duration (500ms) by short circuit at 4kA or 7kA. The result for this test is pass or fail. Passing 4kA results in APC 1 (Arc Protection Class) and passing 7kA results in APC 2. Passing APC 2 often requires combinations of different garments.
Clothing: IEC 61482-2
EN 60903 is a European standard that specifically addresses electrical safety of gloves. This standard tests insulating gloves for different voltages and divides them into 6 classes, namely 00 to 4 (see table below). Want to extend the life of insulating gloves while having the right mechanical protection? Then combine insulating gloves with suitable overgloves.
Class | Maximum AC operating voltage | Maximum DC operating voltage |
00 | 500V AC | 750V DC |
0 | 1000V AC | 1500V DC |
1 | 7500V AC | 11250V DC |
2 | 17000V AC | 25500V DC |
3 | 26500V AC | 39750V DC |
4 | 36000V AC | 54000V DC |
Head protection: EN 50365 & GS-ET-29

European standard EN 50365 applies to electrically insulating helmets for use when working up to a voltage of 1000V AC or 1500 Volts DC.
Face shields provide additional protection against the dangers of an electric arc, such as flying shards or molten pieces of metal. The face shields of this type of helmet are tested according to standard GS-ET-29. This standard, like the box test, tests for either 4kA or 7kA. This also results in either a Class 1 or Class 2 rating.
Foot protection: EN 50321

For work with voltage installations, electrically insulating boots conforming to EN 50321 are applicable. Boots meeting this standard with class 00 provide protection up to a maximum of 500V AC and boots meeting class 0 up to a maximum of 1000V AC.
Our recommendations
Clothing
HAVEP 50292 jacket | HAVEP 80345 pants | Sioen 7227 Nash jacket |
Art. No.: 2.48.749.00 | Art. No.: 2.27.633.00 | Art. No.: 2.42.675.00 |
Gloves
Ansell ActivArmr RIG014Y glove | uvex power protect V1000 glove | Ansell ActivArmr 96-003 glove |
Art. No.: 1.89.907.00 | Art. No.: 1.91.411.00 | Art. No.: 1.89.925.00 |
Head protection
MSA V-Gard 950 Class 1 unventilated safety helmet | MSA V-Gard 950 Class 2 unventilated safety helmet |
Art. No.: 6.16.876.11 | Art. No.: 6.16.876.12 |
Boots
Dunlop Acifort High Voltage safety boot SB |
Art. No.: 5.25.132.00 |
ARC-Configurator
Not only the outer layer should provide protection against an arc; the underlying layers should also provide the worker with additional protection in the event that the hazard penetrates the outer layers. A higher level of ARC protection can be obtained by combining several layers of ARC protective clothing.
Opting for a multi-layer solution also offers workers more flexibility. For example, if they wear an ARC Class 1 long-sleeved polo shirt as a bottom layer AND an ARC Class 1 softshell jacket as a top layer, ARC Class 2 protection level is achieved. So the combination provides a higher level of protection, and one layer can be taken off if only ARC Class 1 is required.
Sioen 581A Telfs Polo shirt | Sioen 9705 Umiat softshell jacket | Sioen 9633 Playford softshell jacket |
Art. No.: 2.60.102.00 | Art. No.: 2.60.683.00 | Art. No.: 2.49.100.00 |
Use Sioen’s ARC configurator to see what clothing you can combine for the different layers to achieve the desired results. This also shows the ATPV and ELIM values; which are also used to determine the required protection of a worker exposed to the thermal risks of an arc.
Need help?
Want advice or additional information on the right products when working with high voltage? Contact us today on T. +31 (0)181 47 50 00. Our enthusiastic team will be happy to tell you more!












