Knowledge base
Understanding hazards and protection for workers
What are chemical hazards?
Chemical hazards are the risks created by the use, storage, production, or processing of chemicals. These hazards can lead to serious health effects, accidents, and environmental damage. Understanding and managing these hazards is important for ensuring a safe work environment and reducing risks to both people and the environment.
Types of chemical hazards
There are several chemical hazards in the chemical sector. We focus on the five most common, give an example for each, evaluate the degree of dangerousness and the impact they can have on workers.
- Toxicity
- Exposure to toxic substances can cause both acute and chronic health effects, such as poisoning, respiratory problems, and long-term organ damage or cancer (RIVM, 2023)
- Example: Benzene is a chemical used in the production of plastics, resins, and synthetic fibers
- Degree of dangerousness: very dangerous ⚠️⚠️
- Exposure to toxic substances can cause both acute and chronic health effects, such as poisoning, respiratory problems, and long-term organ damage or cancer (RIVM, 2023)
- Corrosivity:
- Corrosive substances can cause severe burns on skin contact and damage to eyes and respiratory tract when vapors are inhaled (Arboportaal, s.a.)
- Example: Sulfuric acid is widely used in the chemical industry, for example in the production of fertilizers
- Degree of dangerousness: very dangerous ⚠️⚠️
- Corrosive substances can cause severe burns on skin contact and damage to eyes and respiratory tract when vapors are inhaled (Arboportaal, s.a.)
- Flammability:
- Chemicals that easily catch fire pose a high risk of fires and explosions
- Example: Acetone is a widely used solvent in the chemical industry and in laboratories
- Degree of dangerousness: high danger ⚠️
- Chemicals that easily catch fire pose a high risk of fires and explosions
- Explosiveness:
- Substances that can explode under certain conditions pose a serious physical hazard to employees
- Example: Ammonium nitrate is used as fertilizer and in explosives
- Degree of dangerousness: very dangerous ⚠️⚠️
- Substances that can explode under certain conditions pose a serious physical hazard to employees
- Chemical Reactivity:
- Highly reactive substances can cause unexpected reactions when in contact with other chemicals or with water, leading to hazardous conditions such as explosions or the release of toxic gases
- Example: Sodium is a highly reactive metal often used in the chemical industry
- Degree of dangerousness: high danger ⚠️
- Highly reactive substances can cause unexpected reactions when in contact with other chemicals or with water, leading to hazardous conditions such as explosions or the release of toxic gases
How do you protect yourself from these substances?
Protection from chemicals in industry requires a combination of measures to ensure safety and the use of appropriate PPE. The choice of PPE should always be based on a risk assessment of the specific working conditions and the properties of the chemicals being worked with. It is essential that PPE be used and maintained correctly to ensure maximum protection.
Below we share the most common PPE in this industry and the associated safe work procedures:
PPE
- Respiratory protection:
- Gas and vapor masks: for protection from harmful gases and vapors
- Dust masks: for protection from inhalation of hazardous substances such as powders or fibers
Our recommendations
The 3M visor helmet is combined with the 3M Versaflo motor-powered system that is suitable for use in an ATEX environment and provides long-lasting and optimal protection for the respiratory tract, head and face.
|
|
|
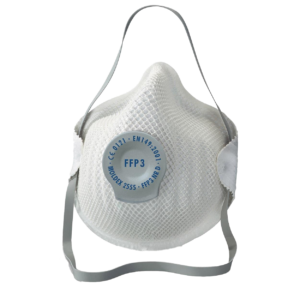
3M M-306 | 3M VERSAFLO TR-819E | MOLDEX 255501 DUST MASK FFP3 NR D WITH EXHALATION VALVE |
- Eye protection
- Safety glasses: for protection from chemical splashes or dust particles
- Face shields: for protection from larger amounts of liquids or as additional protection on top of safety glasses.
Our recommendation:
|
UVEX ULTRASONIC 9302-285 |
- Hand protection:
- Chemical-resistant gloves: made of materials such as nitrile, neoprene, or butyl rubber, depending on the nature of the chemicals being worked with
Our recommendations:
|
|
OXXA® X-PRO-CHEM | ANSELL ALPHATEC |
- Body protection:
- Parka: provides light protection and resists splashes of liquids, making it suitable for everyday use in environments where the risk of chemical exposure is minimal. However, more intense or high-risk chemical work requires specialized protective clothing.
- Coverall: which is specially designed to withstand the specific chemicals being worked with. The coverall provides full body coverage and protection from chemical exposure, which is essential for working safely in high-risk environments.
Our recommendations:
|
|
SIOEN 7223 HEDLAND | DUPONT TYCHEM 2000 C |
- Foot Protection:
- Safety shoes: with steel toecap and chemical-resistant material, are suitable for everyday use
- Safety boots: provide extra protection for specific higher-risk tasks, such as working with larger amounts of chemicals or in areas with high splash
Our recommendations:
|
|
EMMA BILLY SAFETY SHOE | DUNLOP JOBGUARD FULL SAFETY BOOT S5 |
- Hearing protection:
- Earplugs or earmuffs: If the noise level in the workplace is high, such as from the use of machinery.
Our recommendations:
|
|
uvex X-FIT 2112-001 EARPLUG | MSA V-GARD HIGH EAR MUFF WITH HELMET ATTACHMENT |
- Head protection:
- Safety helmets: To protect against falling objects or as protection when working in explosive environments.
Our recommendation:
|
MSA V-GARD 500 UNVENTILATED |
Safe Work Procedures
- Training and Education: ensure that all employees are well versed in proper chemical handling procedures, including the use of PPE and emergency procedures
- Safe Storage: store chemicals in approved, labeled containers in safe, well-ventilated locations according to manufacturer’s recommendations and laws and regulations
- Proper Use: follow all chemical use instructions and avoid unnecessary exposure by using safe work practices
Need help?
Would you like advice or additional information on suitable products for use in the chemical sector? Contact us today on T. +31 (0)181 47 50 00. Our enthusiastic team will be happy to tell you more!